Cosmetic Surgery Art Technique Shiffman Di Giuseppe Download Pdf
Corrective Surgery Art Technique Shiffman Di Giuseppe Download Type Pdf
Review
Liposuction: Concepts, safety, and techniques in body-contouring surgery
Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine June 2020, 87 (vi) 367-375; DOI: https://doi.org/10.3949/ccjm.87a.19097

ABSTRACT
Liposuction is the 2d most commonly performed cosmetic surgery in the United States and the most common surgical procedure in patients betwixt the ages of 35 and 64; practitioners of medicine and surgery will undoubtedly encounter these patients in their practice. This brief review discusses the office of liposuction and fat transfer in artful and reconstructive surgery, equally well as key considerations, indications, and safety concerns.
Primal POINTS
-
The most common area for fat removal is between the inframammary fold and gluteal fold—namely, the abdomen, flanks, trochanteric region, lumbar region, and gluteal region.
-
Liposuction is increasingly beingness used as an adjunct to heighten other aesthetic procedures such equally breast augmentation, cervicoplasty, abdominoplasty, gluteal fat transfer, and body contouring after bariatric surgery.
-
Gluteal fat transfer, popularly chosen the "Brazilian butt lift," is an application of liposuction in which large volumes of fat are transferred from an undesirable area, such as the abdomen or inner thighs, to the buttocks.
-
Noncosmetic indications include management of lipomas, lipedema, and lipodystrophy syndromes.
-
The near mutual complexity is contour deformity.
Suction-assisted lipectomy, more commonly known as liposuction, is an outpatient procedure that removes adipose tissue from the subcutaneous space with the goal of achieving a more than desirable body contour. It is the second almost usually performed cosmetic surgery in the United States and the virtually common surgical procedure in patients betwixt the ages of 35 and 64.one In 2018, surgeons performed 258,558 liposuction procedures, a 5% increase from 2017.2 The number of liposuction procedures increased 124% from 1997 to 2015.three
Liposuction is advantageous in that the removal of fat cells limits future deposition of fatty in those areas.4 Ultimately, liposuction allows plastic surgeons to semipermanently redistribute volume in accordance with a patient's ideal, and with lower complication, morbidity, and mortality rates than with other surgical procedures.
In addition to its utility for purely aesthetic purposes, liposuction is an of import adjunct in reconstructive surgery, particularly of the breast and face up, when harvested fat is autologously reinjected in these tissues. One item procedure ascension in popularity and gaining significant attending in the media is gluteal fat grafting.
This article provides a full general overview of liposuction, including its history, electric current techniques, indications, and safety concerns.
HISTORY
The first effort at fat removal was past Dujarrier in 1921, who operated on the knees and calves of a dancer. Injury to the femoral artery led to amputation of the leg.5 In 1964, Schrudde curetted subcutaneous fat from a patient's leg, but observed pare necrosis in 4 of 15 dissever patients, in improver to hematoma and seroma.half dozen
The era of modern liposuction began in 1975 when Arpad and Fischer pioneered the employ of edgeless hollow cannulas and suction curettage for liposuction on the outer thighs, but the patients ultimately experienced deforming lymphorrhea.seven An important milestone was reached in 1977 when Illouz developed the "wet technique," in which injection of hypotonic saline solution and hyaluronidase into adipose tissue before liposuction reduced hemorrhagic adventure.8 This type of hydrodissection, similar to that used today, preserved neurovascular bundles and enlarged the deep adipose layer for easier aspiration.
In 1983, Fournier used syringes instead of mechanical suction for amend control of negative pressure.9 By 1987, Klein had adult the tumescent technique—a blazon of local anesthesia infiltration that permitted the removal of larger volumes of fat while reducing bleeding.10 Toledo expanded the use of syringes to include diverse gauges and sizes for aspiration of adipose tissue in 1988.11
In the early 1990s, the evolution of ultrasonographically guided liposuction by Zocchi expanded the use of liposuction for previously unfavorable, fibrous areas such every bit the buttocks.12,xiii The development of minimally invasive, light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation-assisted liposuction by Apfelberg, likewise in 1992, prevented destruction of neurovascular structures by cannulas and promoted tissue tightening for an aesthetic event.14 Recently, the development of power-assisted liposuction has further expanded and improved this procedure, increasing the popularity and use of liposuction.fifteen
Cosmetic INDICATIONS
Liposuction is used to achieve torso contouring by removing backlog fatty deposits in undesirable areas of the torso. Fat is suctioned from demarcated areas in the body amenable to contouring.
The most mutual area for fat removal is between the inframammary fold and gluteal fold—namely, the abdomen, flanks, trochanteric region, lumbar region, and gluteal region (Figure 1). Other areas of fat removal include the breasts (eg, breast reduction surgery), thighs, and calves.
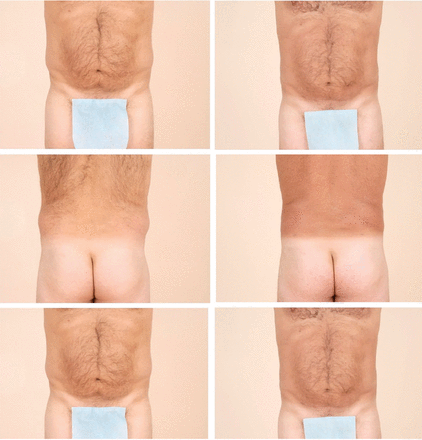
- Download figure
- Open up in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Figure ane
Left: Preoperative appearance of a 52-year-sometime man who presented for liposuction of localized adiposity inside the abdomen and bilateral flanks. Right: The same patient 6 months later on subsequently removal of one.4 L of adipose tissue.
The site of incision is an of import anatomic consideration, and the surgeon should select regions where the surgical scar, although minor, can be hidden by clothing, as well as locations conducive to broad fanning of the cannula during the process.
There are 5 zones in which superficial subcutaneous tissues attach to underlying deep fascia of musculus: the lateral gluteal low, gluteal crease, distal posterior thigh, midmedial thigh, and inferolateral iliotibial tract. Considering these zones define the natural shape of the body, suctioning from these areas increases the risk of contour deformities.16 Ideally, patients have acceptable skin elasticity and are within 20% to 30% of their ideal torso weight to achieve desired aesthetic outcomes.17
Liposuction is also increasingly being used equally an adjunct to enhance other artful procedures such equally breast augmentation, cervicoplasty, abdominoplasty, gluteal fat transfer, and trunk contouring for postsurgical bariatric patients (Effigy ii and Figure three).xviii Liposuction can also be used to promote gender-specific features.19 In women, the goals of liposuction are to promote shapely contours of the breasts, waist, hip, and buttocks. In men, liposuction aims to accomplish upper torso dominance, such as removing excess flank adipose tissue ("love handles").
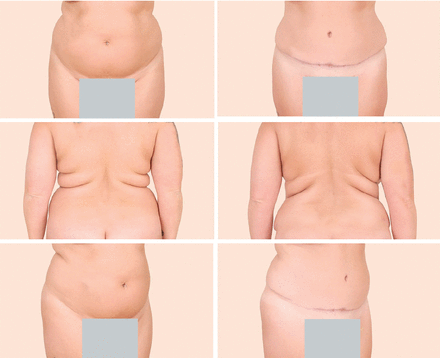
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Figure 2
Left: A 38-yr-old adult female who presented with excess peel and adiposity of the anterior abdomen and backlog adipose tissue in the bilateral upper back and hips. Right: The same patient 5 months later after full cosmetic abdominoplasty and liposuction of the bilateral upper back and hip areas (with a full of ii L of tissue removed), illustrating that these procedures may be combined safely and yield satisfying results.

- Download figure
- Open up in new tab
- Download powerpoint
Figure iii
The same patient from Figure two, now almost xix months afterwards surgery only having lost weight, demonstrating stable long-term results after abdominoplasty and liposuction. Note the stable improvement in bilateral flank and upper-back adiposity.
GLUTEAL Fat TRANSFER
Gluteal fatty transfer, popularly chosen the "Brazilian butt lift," is an application of liposuction in which big volumes of fat are transferred from an undesirable area, such as the abdomen or inner thighs, to the buttocks.20 Fat is first removed past liposuction (the volume of which varies widely and remains largely based upon the patient's preoperative anatomy) and is then used to augment the contour of the buttocks commensurate with the patient'southward desires and anatomic deficiencies.21,22
High-volume fat transfer, defined as a volume greater than 1,000 mL per buttock, has historically been associated with a higher risk of infection at the graft site and seroma germination at the harvested site. Newer testify suggests loftier-book buttock fat transfer may be safe and constructive with proper technique.23 Thus, the contour is improved in both the donor region, such as the waist, and the recipient region.
The popularity of gluteal fatty transfer is rapidly increasing due to shifting beauty standards in American culture and attention from celebrity figures. More 26,000 gluteal fatty transfer procedures were performed in 2018, a sixteen% increase from the previous year, and a 132% increase from 2013.3,24 Withal, reports of fatal pulmonary fat embolisms following injury to gluteal veins and an estimated mortality charge per unit of 1 in 3,000 from this procedure warrant continued investigation about its safety and ideal technique.25
The Multi-Society Gluteal Fat Grafting Task Force26 was established to investigate and improve patient safety of this process, and electric current research including anatomic studies as well as educational symposia are ongoing. Risks and alternative methods such as gluteal implants must exist discussed with the patient before this process. Moreover, as with any aesthetic or reconstructive procedure, the American Society of Plastic Surgeons recommends that patients seek consultation from a board-certified plastic surgeon.
NONCOSMETIC INDICATIONS
Liposuction is likewise existence used for reconstructive purposes, including direction of the following disorders:
-
Lipomas and angiolipomas, with minimal to no scarring
-
Lipedema, in which subcutaneous fatty deposition in the lower limbs tin can interfere with daily activities such every bit walking; in these patients, liposuction tin improve mobility27
-
Lymphedema, specially if it is refractory to traditional conservative treatments
-
Lipodystrophy syndromes, which are congenital or acquired diseases of fatty cloudburst; liposuction with autologous fatty transfer can replace loss of fatty in areas such as the feet or buttocks to salve concrete discomfort28
-
Cervicodorsal lipodystrophy associated with Cushing syndrome and use of HIV medications29
-
Gynecomastia in men and macromastia in women, in conjunction with mammoplasty. Additionally, liposuction tin can be used to:
-
Reduce backlog fat deposits at surgical sites in obese patients who are undergoing tracheostomy, colostomy, or urostomy procedures • Reduce the corporeality of subcutaneous fatty in flaps created for reconstructive procedures, thereby improving artful results
-
Collect harvested fatty to "lipofill" in breast reconstruction, burns, and scars because developed adipose-derived stem cells are contained therein.thirty
Although no accented contraindications exist for liposuction, relative contraindications should be considered during the patient evaluation.31 Anticoagulants and medications that interfere with lidocaine metabolism should exist stopped earlier liposuction.32 Poor skin firmness and elasticity in elderly patients would lead to poor skin draping postoperatively and potentially increase patient dissatisfaction.
Further, reasonable expectations must be established, and patients with trunk dysmorphic disorder may require a psychiatric consultation before surgery. Patients with diabetes mellitus, cardiac disease, and liver disease may demand medical clearance before surgery at the discretion of both the surgeon and the facility where the procedure is to accept place. Lastly, as has been discussed elsewhere in the surgical literature, poorly controlled diabetes increases the hazard of infection.
TECHNIQUES
The most common technique remains the traditional suction-assisted lipectomy (Table 1).33–36 Pocket-size-book liposuction procedures in which a maximum of 1,000 mL of fat is removed can be performed with local anesthesia. Although there is no maximum volume of fat that can be removed in a single setting, the risk for seroma and fluid imbalance increases along with the volume of fat that is removed.
Table 1
Liposuction techniques
Megaliposuction, a procedure in which an amount greater than 10% of body weight is removed, can be safely performed by an experienced surgeon. Large-volume liposuction procedures should be performed with general anesthesia.19 Harvested fat may be used for subsequent fatty transfer.xix
The advantages of liposuction are short surgery time (typically nether 3 hours, depending on the extent of fat removal) and concomitant procedures. In add-on, patients undergoing liposuction have a brusk recovery menstruation, unobtrusive scars, permanent results, depression complication rates, and low morbidity and bloodshed rates relative to other surgical procedures. Because adipocytes are removed, further storage of fatty in those areas is limited, leading to high patient satisfaction with long-term results.37
More research is needed to make up one's mind the caste of fat reaccumulation in the treated area and redistribution to nontreated areas.38,39 Equally expected, weight gain can still occur, and the patient should be advised to maintain a well-balanced nutrition and do regimen.
RISK FACTORS
Patients with cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, diabetes, and vascular illness face a greater chance with this procedure. Tobacco use is a risk gene for surgical complications.40,41 Ongoing infections before the process, specially nigh the area of the liposuction site (eg, cellulitis), would crave treatment with antibiotics and resolution of infection before surgery. Previous venous thromboembolism, eg, pulmonary embolism, may also increase the risk of surgical complications.
COMPLICATIONS
Complications are relatively uncommon in liposuction and of low run a risk relative to other procedures.42 In one written report, the overall complexity rate was 2.4%.43 The complication rate was higher (iii.5%) when liposuction was combined with other procedures, whereas liposuction as a alone process had a complication rate of only 0.7%.41 Complications include ecchymosis, edema, surgical site infection, seroma, hematoma, and venous thromboembolism (Table two).43
TABLE two
Complications of liposuction
The most common complexity of liposuction is contour deformity. As many every bit 9% of patients may study soft-tissue depressions or elevations, pare panniculus, folds, or wrinkles.44 Profile deformities can be prevented by using smaller bore cannulas, avoiding suctioning from superficial layers, employing a "crisscrossing" technique, and allowing slight undercorrection for postoperative fatty lysis.45
Seroma and hematoma are also rare complications of liposuction.46 Seromas, which are collections of serous fluid resulting from breakdown of the gristly tissue network, may develop from initial blind cannula injury to pocket-size perforating vessels or lymphatic vessels.31 Use of progressive tension sutures—primarily a technique to address dead infinite in surgeries such equally abdominoplasty ("tummy-constrict")—has been shown to reduce the rate of seroma from ix% to 2%.46
Wound infection is reported in fewer than 3% of inpatient liposuction cases and in approximately 1% in outpatient surgeries.47 Low infection rates can be attributed to surgeon expertise, proper rubber antibiotics, and sterile technique, amid other factors. Although uncommon, early-stage wound infections (ie, cellulitis) may develop into more astringent sepsis or necrotizing fasciitis—the latter of which is a surgical emergency.48
A 2018 written report estimated that after liposuction with or without subsequent fat grafting, at least 17 patients accept experienced clinically significant fat embolization, or fat embolization syndrome.49 However, more than recent data suggests that worldwide, fatal and nonfatal fat embolism, peculiarly after gluteal fat grafting, may exceed 135 cases.l
Although fat embolism is rare, its mortality charge per unit of 10% to 15% warrants conscientious postoperative monitoring for rapid detection and treatment, and it has been reported to occur inside 12 to 72 hours later on surgery. 50,51 As described, gluteal fatty transfer is the only procedure with a higher take a chance of fatal fat embolism, and is however considered to take the highest mortality charge per unit of any aesthetic procedure.52
The incidence of venous thromboembolic events (deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) later on liposuction is low at 0.03%.53,54 Pulmonary embolism is the most common cause of death after this process, which carries an overall mortality rate of 0.01%.54 Same-day ambulation afterwards liposuction surgery is encouraged to forbid thromboembolic events.
Every bit with any surgical process, liposuction causes a transient elevation of astute inflammatory markers (interleukin 6, C-reactive protein), but there is no increased take chances of progression to renal disease or chronic inflammation.55 Some studies advise that, due to permanent removal of adipocytes, the long-term metabolic benefits of liposuction include improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation. However, more studies are warranted.56
Systemic complications that arise weeks to months after surgery include edema, lymphedema, wound dehiscence, hypertrophic scar formation, ecchymosis, and skin laxity. Blind cannula injury tin can pb to abdominal wall injury, bowel perforation, or vessel injury. Although uncommon, skin devascularization and skin necrosis can occur if the surgeon suctions too closely to the skin undersurface and injures the dermal plexus.57
Chest augmentation with autologous fat transfer may lead to fat necrosis that mimics microcalcifications suspicious for breast cancer on mammographic imaging.58 However, the incidence of these imaging findings is similar to those in patients without fat transfer, and thus, breast augmentation does not hinder detection of chest cancer.
FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Liposuction can improve body contour and reduce body mass index, and advances are continually beingness developed. Due to the benefits of long-term weight redistribution, low surgical risk, and brusque operation time, patients seeking body contour changes will go along to pursue liposuction. The long-term effects on metabolic sequelae such every bit insulin sensitivity are however being actively researched.59,60
Noncosmetic indications are likewise expanding, specially fat grafting for breast, facial, and pedal reconstruction.61 Although liposuction can address a broad multifariousness of needs spanning from corrective to reconstructive purposes, the procedure is rarely covered by Medicare or third-party insurance plans, fifty-fifty for issues that cause functional impairment.62
Inquiry is existence performed in noninvasive body contouring such as cryolipolysis, which may decrease subcutaneous fatty deposits while providing dermal tightening with no surgical scars.63,64 Cryolipolysis (CoolSculpting), deoxycholic acid subcutaneous injection (Kybella), and radiofrequency skin-tightening (Thermage) are nonsurgical volume-reduction and tissue-tightening procedures that address dissatisfaction with body contouring simply remain beyond the scope of this manuscript. We mention them for the sake of completeness.
- Copyright © 2020 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.
REFERENCES
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery'south Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank: Statistics 2018. Aesthet Surg J 2019;39(suppl_4):ane–27. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjz164
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
- ↵
Source: https://www.ccjm.org/content/87/six/367
Posted by: marianomarianoreaumee0303713.blogspot.com
hernandezandem1997.blogspot.com
Source: https://marianomarianoreaumee0303713.blogspot.com/2021/12/cosmetic-surgery-art-technique-shiffman.html
0 Response to "Cosmetic Surgery Art Technique Shiffman Di Giuseppe Download Pdf"
Post a Comment